Learn About The Ground-breaking Futuristic Dawn Spacecraft!
Orbiting Protoplanets Vesta And Ceres
Learn Fun Facts about the groundbreaking Dawn Spacecraft and its mission to explore the two largest asteroids Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. Learn about how Dawn revealed the secrets of these worlds and what they can tell us about the solar system’s formation. Launched in 2007, Dawn would become the first to orbit an asteroid and the first to orbit two on the same mission! Dawn also used futuristic Ion propulsion thrusters to get around; a truly remarkable mission!
Fast Summary Facts About The Dawn Mission
- Type: Multi-target orbiter
- Status: Complete
- Destination: Asteroid Vesta and dwarf planet Ceres
- Launch Location: Cape Canaveral, Florida
- Launch Date: September 27th 2007
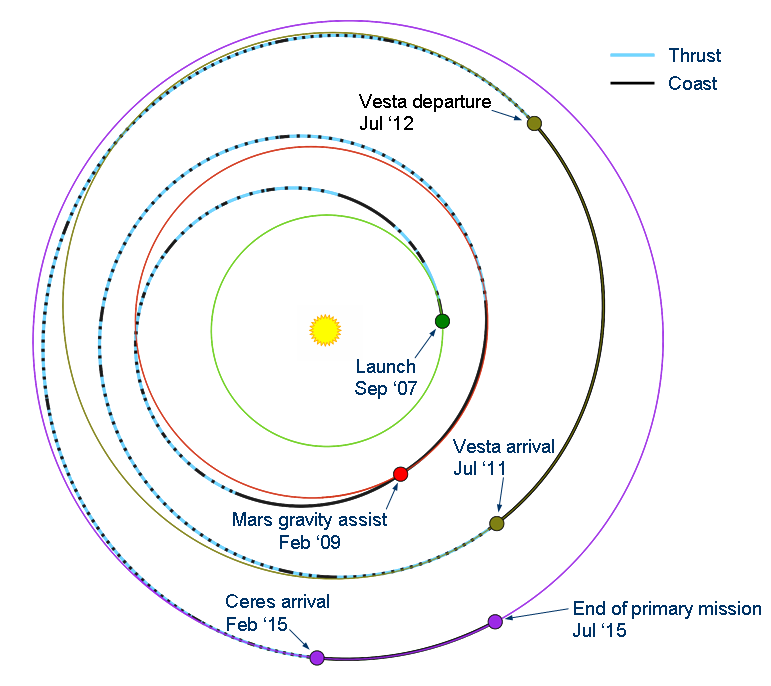
- Planet Mars Flyby: February 18th 2009
- Vesta Orbit Insertion: July 16th 2011
- Ceres Orbit Insertion: March 6th 2015
- Mission Duration: 11 Years
Interesting Fun Facts About The Dawn Mission!
- The Dawn mission is part of NASA’s Discovery Program which is a series of lower-cost space missions exploring the solar system.
- Dawn's scientific objectives were to study the asteroid Vesta and dwarf planet Ceres (the inner solar system’s only dwarf planet) to reveal their secrets about the formation of the solar system.
- The spacecraft carried science instruments such as high-resolution cameras, spectrometers and a gamma-ray/neutron particle detector.
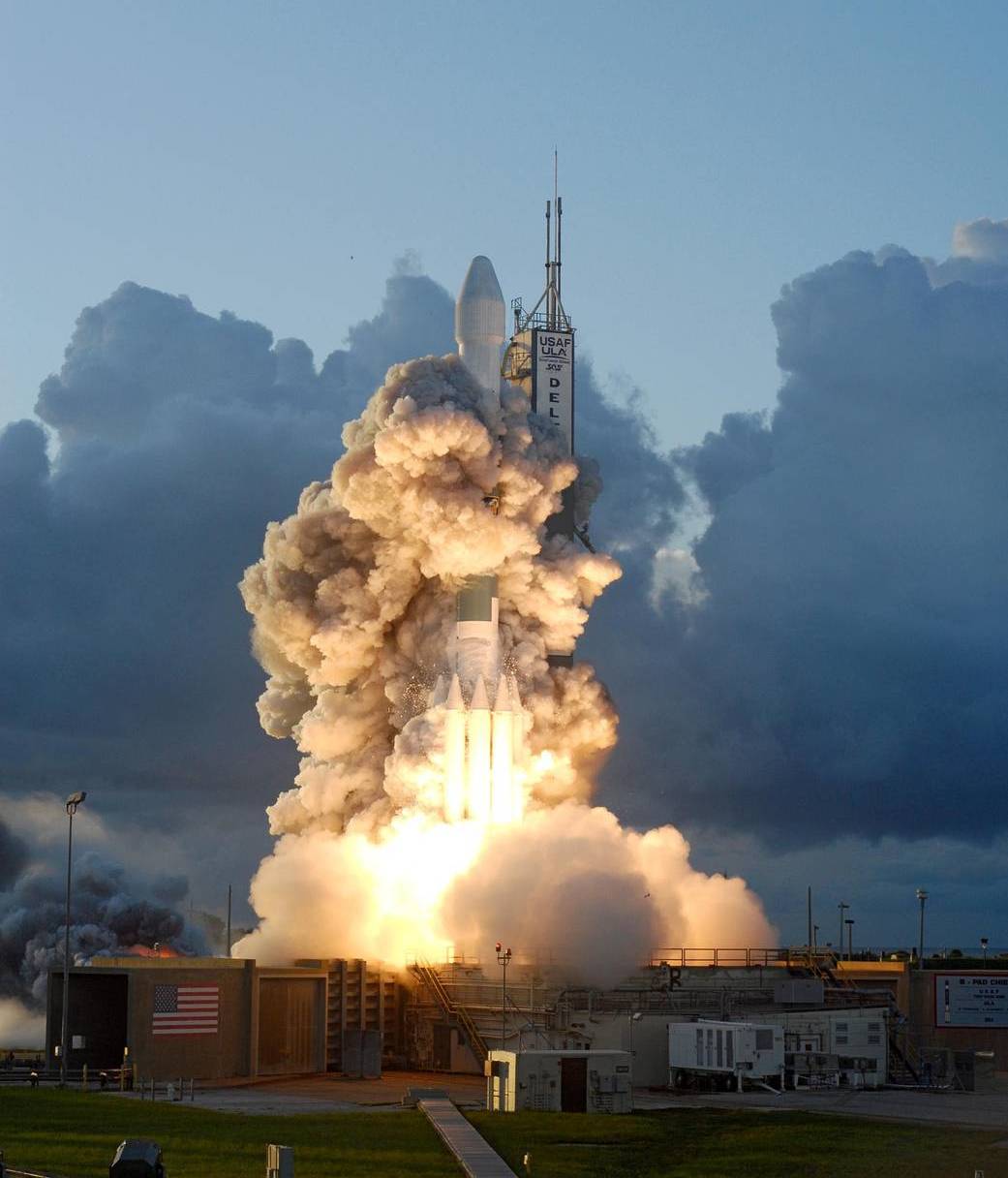
- The Dawn spacecraft was launched atop a Delta II rocket and weighed over 1,217 kilograms (2,685 lbs).
- The four-year cruise through space, around the Sun, took Dawn to within 549 kilometres (341 miles) of Mars’ surface during a planned gravity assist flyby.
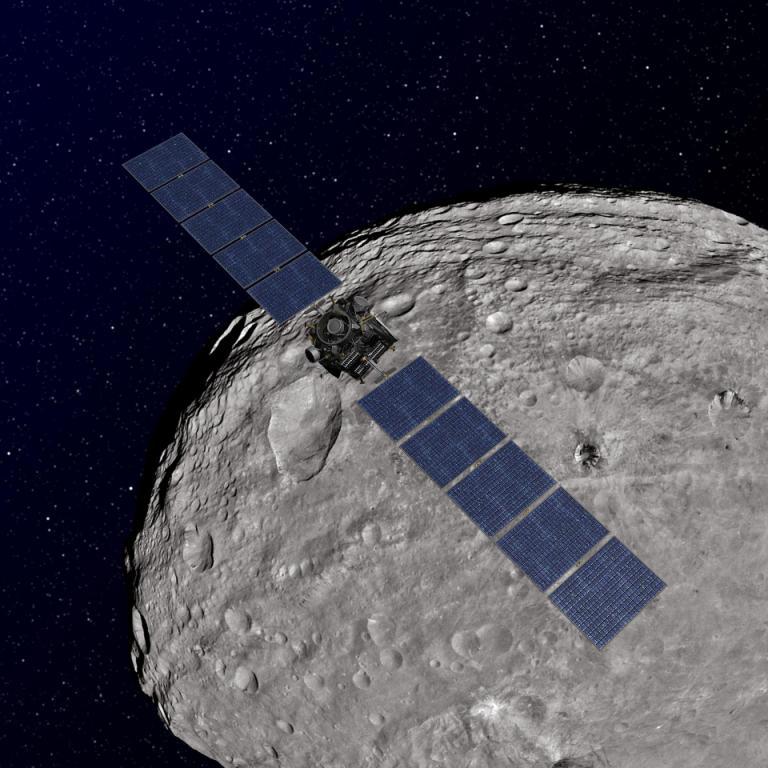
- Vesta and Ceres orbit in the main asteroid belt where sunlight is weaker than near Earth. The spacecraft was also designed to consume a lot of electrical power. This is why Dawn’s solar panels are relatively big, stretching nearly 20 metres (65 feet) from tip to tip when fully extended!
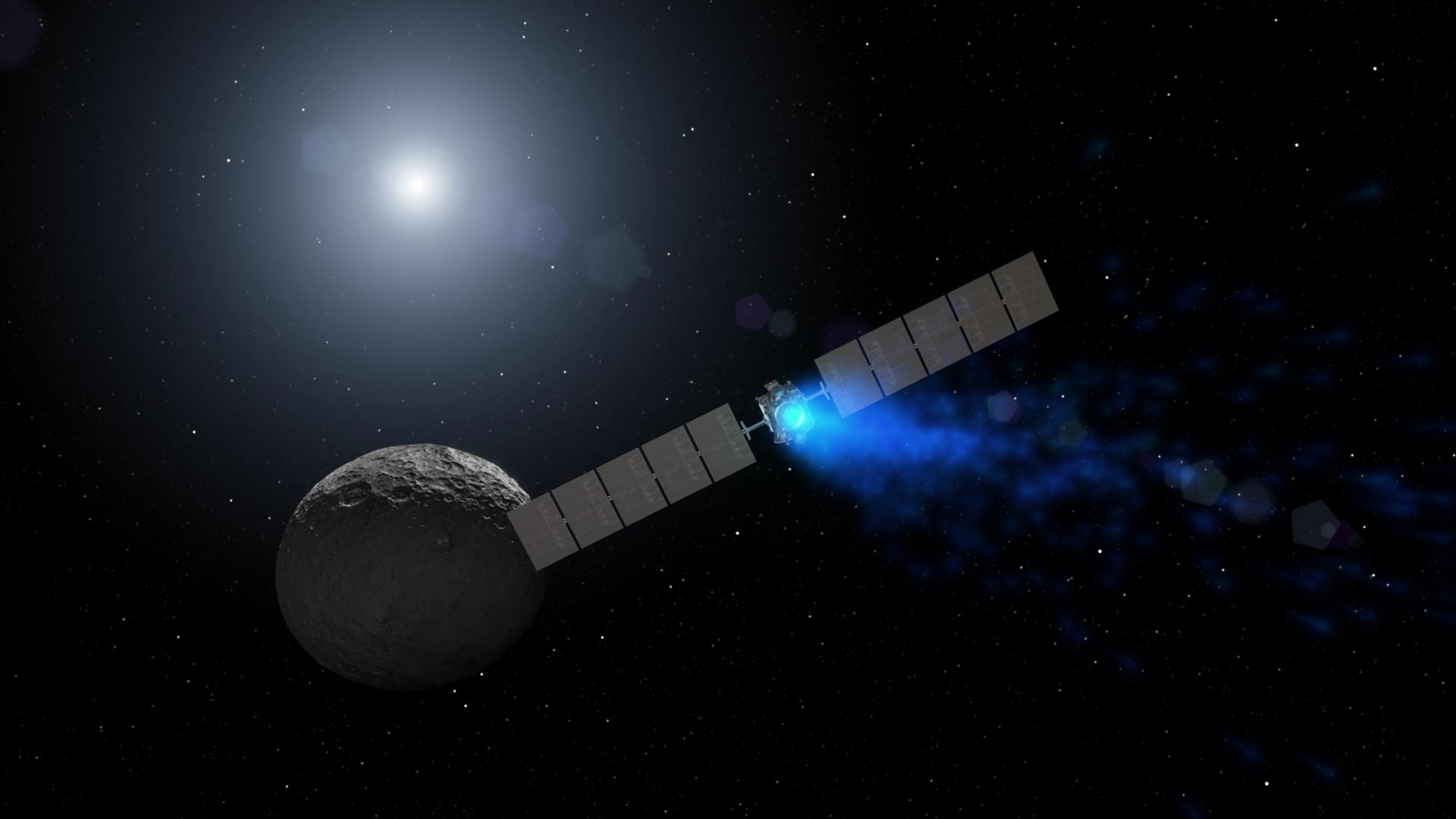
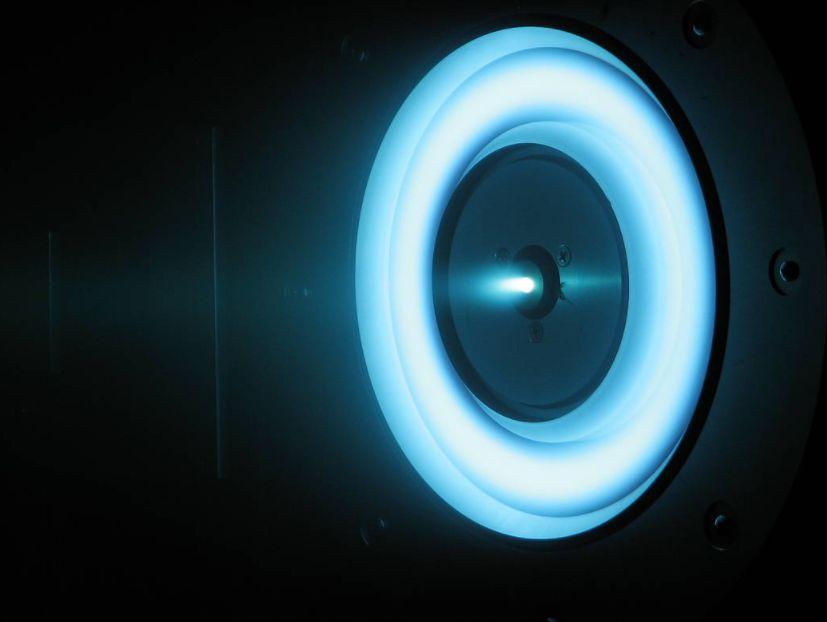
- The Dawn spacecraft used, for the first time on an exploration mission, a futuristic type of rocket propulsion called ion propulsion. The three ion thrusters use Xenon gas as fuel. The ion thrusters utilize electrical power to accelerate ions to a tremendous speed; providing a source of stable low thrust.
- Dawn’s solar-powered ion propulsion holds the record for changing a spacecraft's speed the most in space exploration history – over 11 km/s! The ion drives accumulated over 5 ½ years of continuous thrust!
- While in orbit around Vesta, Dawn confirmed that Vesta was the source of a type of meteorite (HEDs) that had been blasted off the asteroid and fallen to Earth.
- Dawn orbited the asteroid Vesta for 417 days before departing for Ceres.
- A major and unexpected discovery was made while in orbit around Ceres. Dawn discovered that it was once an ocean world which has since either frozen underground or evaporated into space, leaving highly reflective salts which Dawn returned photos of.
- The Dawn spacecraft achieved three major ‘firsts’ for space exploration;
- The first spacecraft to orbit a main belt asteroid.
- The first to visit and study a dwarf planet.
- And the first mission to orbit two separate objects in space!
- The spacecraft ended its mission when its hydrazine fuel, used for orientating itself, ran out. It will now remain in a stable orbit around Ceres for millions of years!
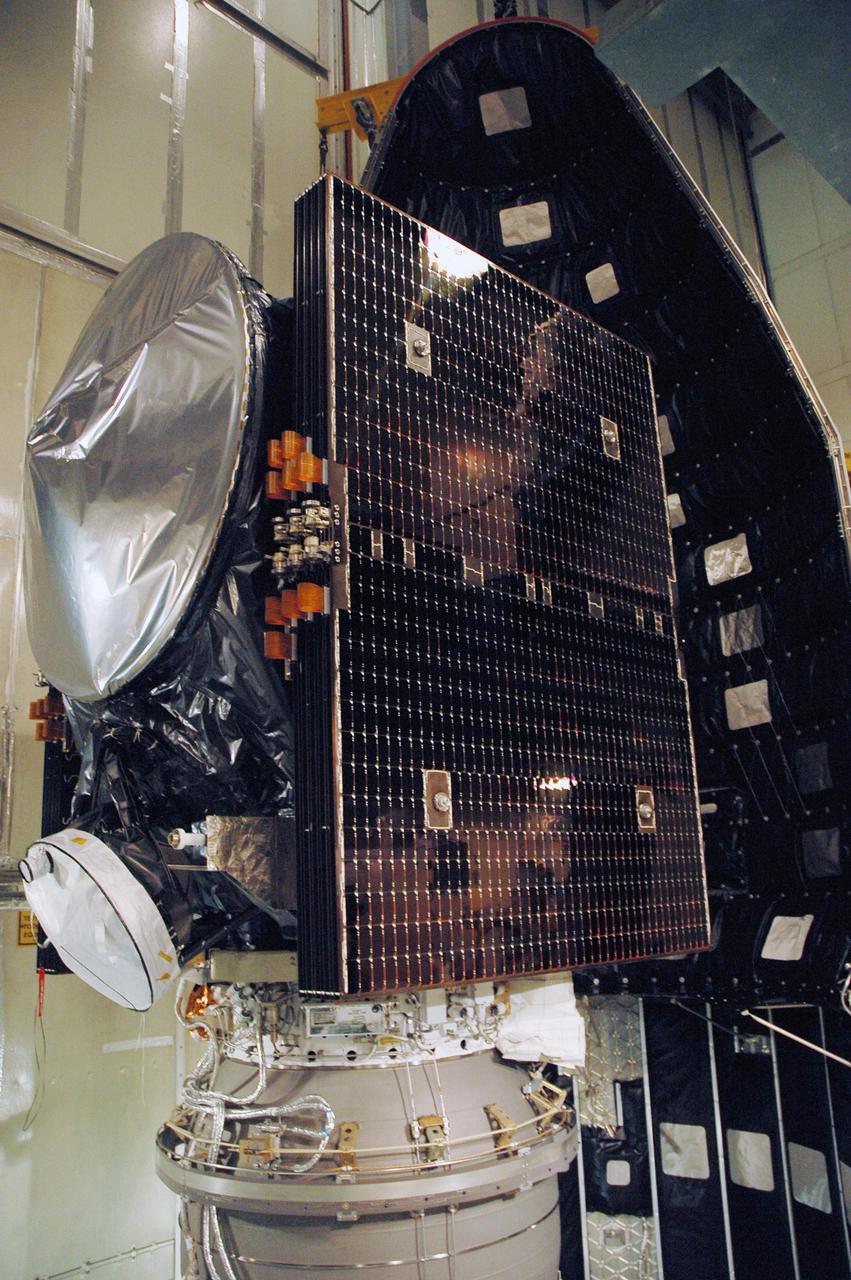




Ready for Launch
Dawn Launch
Dawn's Journey
Ion Engine
Dawn At Vesta
Ion Propulsion
Ceres From Hubble